1. What is information architecture and what is information infrastructure and how do they differ and how do they relate to each other?Information architecture is where and how important information is maintained and secured e.g. customer’s records. It is the overall plan of how the organisation is going to configure IT systems. Information infrastructure composes of the hardware, software and telecommunications equipment that when combined, it is a backbone for the business in achieving its goals.
2. Describe how an organisation can implement a solid information architecture:An organisation can implement an information architecture through the following:
• Back up and recovery
• Disaster recovery
• Information security
• Making IT affordable
• Making information architecture more responsive
• Improve productivity
• Create competitive advantages
• Generate growth
• Generate new revenue systems
• Optimise supply chain
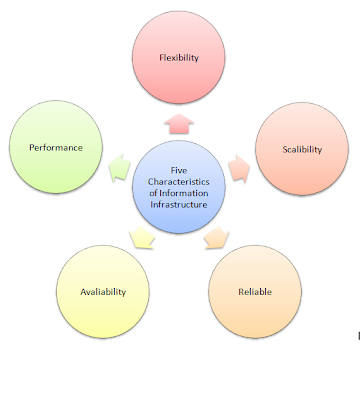
3. List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture:
1. Flexibility – In order to adapt to changes, businesses must be flexible.
2. Scalability – A system needs to be able to become accustomed to risen requirements such as industry, market and economic growth within an organisation.
3. Reliability – Are all systems working properly? Is the correct information given? If information is not sufficient or undependable it can create an impact on important business decision making.
4. Availability – This is where systems can be accessible by members of the organisation.
5. Performance – Assesses the system’s speed of a process or transaction. If performance is low, this can have negative consequences of the business in general.
4. Describe the business value in deploying a service oriented architecture:A service oriented architecture is using different systems to meet different demands. A service does the same thing over and over again and can be applied to many situations.
5. What is an event?This refers to something in a system that tells something has happened and provokes events to occur. It is also the locating of threats and opportunities and informs the appropriate people to take action on the information.
6. What is a service?This is where an organisation has to engage to an audience and if a service wants productivity their service needs to be reusable. This contains directions which in return can be used again and is in similarity to a software product.
7. What emerging technologies can companies use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure?There are two ways in which companies can use emerging technologies to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure in an organisation. These predominantly compose of virtualisation and grid computing. Virtualisation is described as structure for the portioning of computer resources into numerous implementation surroundings. Through the utilisation of virtualisation, all aspects of the organisation such as people, processes and technology are able to come together and work in a competent manner which will in turn amplify levels in terms of service. Grid computering refers to the combining of geographically spreaded computering, storage and network resources that synchronise to bring enhanced performance abilities, better service quality, improved operations and data access in which can be effortlessly accessed.
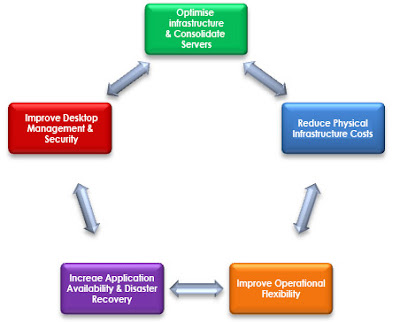
Benefits of Virtualisation in an organisation.
Baltzan, Phillips, Lynch, Blakey. 2010. Business Driven Information Systems. McGraw Hill. Sydney, Australia.
Highlander Direct. 2007. Virtualisation.http://www.highlanderdirect.com/virtualisation.htm. Date Accessed: 30th May 2010.









.gif)











